Hill Engineering was recently admitted to the Forging Industry Association (FIA). For more than 100 years, the FIA has been helping forging companies in North America to increase their global competitiveness. FIA’s producer member companies manufacture approximately 75% of the custom forgings volume produced in the United States, Canada and Mexico. Its supplier members manufacture materials and provide services used by the forging industry. Together, FIA’s 200 members comprise the only trade association dedicated to promoting and serving the forging industry in North America.
Hill Engineering was admitted to the Forging Industry Association due to our strong commitment to supporting the forging community with products and services related to forging design, residual stress measurement, and forging modeling.
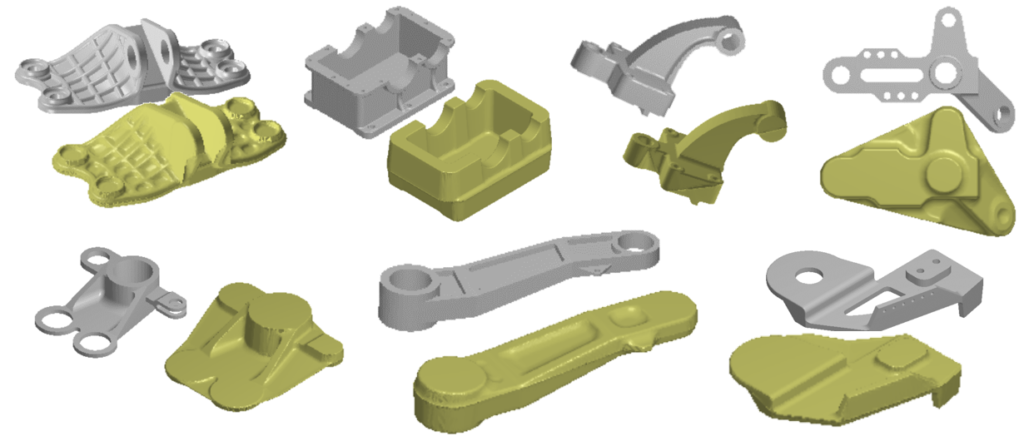
Rapid Forge Design™ software is an automated tool for fast and reliable design of 2-piece, closed-die impression forgings. Rapid Forge Design™ reads the final part geometry and automatically designs a forging according to accepted industry guidelines and user inputs. Rapid Forge Design™ is intended for use by forging suppliers and forging consumers/OEMs.
For materials engineers, designers and managers seeking residual stress measurements, Hill Engineering is a trusted source for a broad range of best in class residual stress measurement capabilities. Focusing on your engineering challenge, Hill Engineering works with you on technique selection, to determine the best residual stress measurement technique to address your needs, and we tell you exactly what to expect before we start the job.
Hill Engineering offers modeling services related to heat treatment and mechanical stress relief. Aluminum alloy heat treatment is a three-step process designed to achieve the desired properties. The process involves: 1) solution heat treatment (SHT) at an elevated temperature below the melting point, 2) quenching in a tank of fluid (e.g., 140-180°F water), and 3) age hardening. While providing good properties, the heat treatment has the negative side effect of creating bulk residual stress and distortion. These side-effects are a direct result of non-uniform cooling during the rapid quench. One approach to mitigate this problem is the application of a post-heat treatment mechanical stress relief process. In addition to modeling the heat treatment process, our analysis tools can support evaluation and optimization of mechanical stress relief processes.
If have any questions about our forging related services, please do not hesitate to contact us. We would be happy hear from you.
