Aluminum alloy heat treatment is a three-step process designed to achieve the desired properties. The process involves: 1) solution heat treatment (SHT) at an elevated temperature below the melting point, 2) quenching in a tank of fluid (e.g., 140-180°F water), and 3) age hardening. While providing good properties, the heat treatment has the negative side effect of creating bulk residual stress and distortion.
Our latest case study highlights Hill Engineering’s quench process simulation capabilities and how they can be utilized to reduce uncertainty in planning and improve processes through validated models. The study focuses on modeling of the heat treatment process for a representative aluminum forging.
Click the link above to read the full write-up, or visit our case study page to read through any of our previous work highlights. If you have further questions, don’t hesitate to contact us for more information.
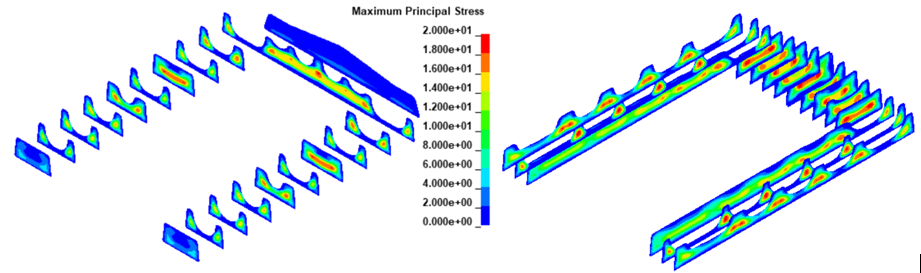
Illustration of predicted post-quench bulk residual stress in an aluminum forging